Nepali Herbs
Nepal is a treasure trove of nature, such as spices and herbs which are directly related to human life and health. According to the Department of Botany, Nepal, seven hundred species of herbs are currently being used as medicine in Nepal. Most herbs used as medicine are produced in the Karnali region and the least in the western region.
Among the significant Nepali herbs produced in the country include Asuro, Amala, Harro, Barro, Kurilo, Datura, Bar, Peepal, Tulsi, Aloe Vera, Yarsagumba, Neem, Chandan, Turmeric, Rudraksha, etc. Still, there are many more herbs that remain to be identified. Unfortunately, most of these herbs are exported to India and China due to the lack of Ayurvedic companies in the country.
And the irony is neighboring nations are strengthening their economy with Nepali herbs while Nepal remains ignorant of its own richness.
However, during the COVID 19 pandemic, the usage of herbs, their knowledge, and their recommendation increased in Nepal.
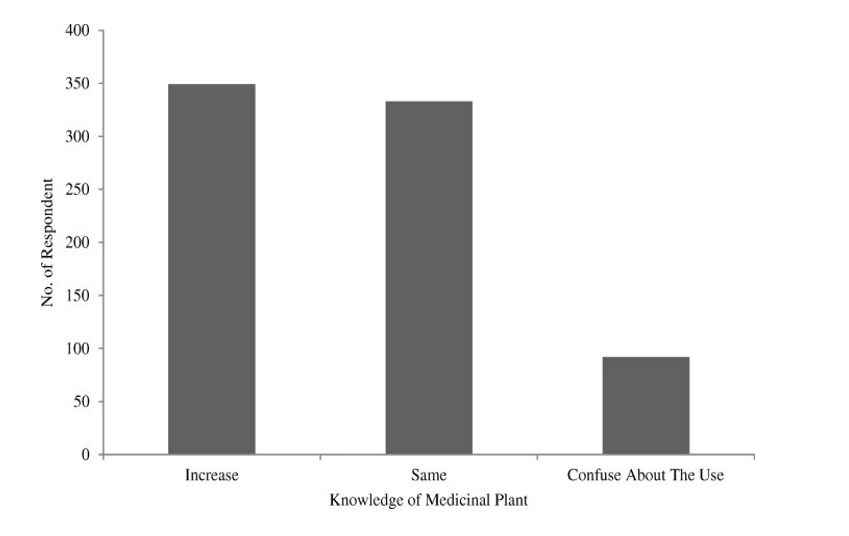
Source: Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine
This article will highlight major Nepali herbs and their benefits to your health.
- Tulsi (Holy Basil)
Information
| Scientific Name | Ocimum tenuiflorum |
| Grown in | Jhapa, Morang, and Illam |
| Flowering period | June to August |
| Flower color | Purple or white |
| Types | Dark tulsi is known as Shyama or Krishna tulsi, and light tulsi is known as Rama tulsi |
| Parts used | Root, stem, and leaves |
Tulsi is regarded as the most sacred medicine among medicinal herbs. It has been used in Ayurveda for thousands of years to treat malaria, colds, asthma, inflammation, skin ailments, indigestion, and mental fatigue.
The word tulsi is translated as incomparable. This name is easy to explain since tulsi positively affects human health in general, making it almost incomparable with other herbs.
In Hinduism, it is an incarnation of Goddess Lakshmi and is worshiped as a sacred plant. Holy basil is still planted in large numbers around Hindu temples, as it is believed to repel the gods of death and protect the home.
Holy basil grows to a height of 30 to 60 cm, and its leaves have a strong scent. The stems have many fine hairs and many branches.
Health Benefits:
- Tulasi helps to cope with stress. It has adaptogenic properties, which can help the human body adjust to a stressful environment.
- The ether (diethyl ether) contained in the tulsi leaves has a strong antibacterial effect and prevents the development of bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli.
- These active ingredients of holy basil enhance immune function and metabolism, prevent lifestyle-related diseases, influenza, and colds, and relieve physical ailments such as headaches, respiratory diseases, decreased liver function, gastritis, swelling, and sensitivity to cold.
- Several studies show that holy basil improves the condition of people with diabetes by helping control weight and cholesterol and regulating insulin levels in the blood.
- Yarsagumba
Information
| Scientific Name | Ophiocordyceps sinensis |
| Found in districts | Dolpa, Mugu, Kalikot, Jumla, Darchula, Bajura, Bajhang, Jajarkot, Rukum, Rolpa, Myagdi, Baglung, Parbat, Mustang, Manang, Rasuwa, Ramechhap and Sankhuwasabha |
| Harvesting period | May and June |
| Color | Brown |
| Other name | Jivanbuti and kira jadi |
| Parts used | Whole |
This amazing medicinal herb in the form of mushroom grows in Tibet, Bhutan, Nepal, and India (its northern part). The mushroom resembles a caterpillar in its appearance. The herb held the greatest position in ancient Chinese treatises.
When the mushroom season begins in Nepal, almost the entire population of the villages searches for it. Because of its highly valuable properties, the herb is sought by nations like China, America, and Europe. Thus, the Nepal government has introduced a tax of $70 per person who collects it.
Nepalese people who harvest yarsagumba sell the herb for USD 700 per kg, while in the international market, the herb is sold at approximately $3,000 per, making it the most expensive mushroom in the world.
Health Benefits:
- Yarsagumba is beneficial for those suffering from weak erectile function as it has a stimulating and healing effect on the functions of the reproductive system.
- It promotes the immune system preventing autoimmune diseases.
- The herb is available in the form of a dietary supplement that has antimicrobial properties.
- It helps in the dilation of constricted heart vessels, lungs, and brain, improving the blood supply to these vital organs.
- It also promotes cell resistance to decay due to its high antioxidant properties.
- Yarsagumba promotes the metabolic function of the body stabilizing the lipid amount in the blood and reducing blood cholesterol level.
- Rudraksha
Information
| Scientific Name | Elaeocarpus ganitrus |
| Found in | Bhojpur and Sankhuwasabha districts |
| Flowering period | June |
| Color | Blue |
| Other name | Blueberry beads |
| Parts used | Seed |
With incredible health benefits, Rudraksha beads are popular among Hindu believers due to the religious faith associated with them. The word Rudraksha refers to the eye of God Shiva. Hindus believe that the beads are the tears of God Shiva which when fell form the sky turned into Rudraksha tree.
Rudraksha is a tree with hard trunks and usually lives in tropical climates. The leaves are small, elongated, and have a unique color, which is green when young and red when they age.
The ripe fruit will be purple or dark blue. The fruit seeds are uniquely patterned, commonly used as Japa mala (Meditation garland) and certain accessories.
Hindus fully believe in the tree’s seeds as a blessing from Lord Shiva. Therefore, Hindu believers wore Rudraksha seeds as bracelet and use it as Japa Mala.
Health Benefits:
- The first benefit of Rudraksha is improved brain function. It is stated that using Rudraksha beads will activate the brain function more efficiently.
- The Rudraksha beads prevent the heart diseases and keep it healthy. After drinking Rudraksha bead tea, consumers feel an improvement in their heart condition.
- With a great combination of nutrients, Rudraksha beads effectively protect against bacteria in our bodies.
- The nutrient content in the Rudraksha bead helps reduces blood pressure if it is high. Meanwhile, the Rudraksha beads’ nutrients will help stabilize your blood pressure if your blood pressure is low.
- Datura
Information
| Scientific Name | Datura stramonium |
| Found in | All over Nepal |
| Flowering period | May and April |
| Color | White, black, light purple, or light pink |
| Other name | Thorn apple, angel’s trumpet, and Jamestown weed |
| Parts used | Leaves, fruits, flowers, stems, or roots. |
Datura are among the most popular tub plants , which delight with their stately growth and unique flowers from the end of May. Because of the large trumpet-shaped flowers, the nightshade family is also called angel’s trumpets. The name Datura goes back to the shape of the fruit.
In addition to the abundance of flowers, the fragrant blossoms should be emphasized. If the water supply and temperature are right, Datura grow into mighty plants that are a feast for the eyes for many years in summer.
Among all the datura species, black datura holds religious importance in Nepal. According to the Hindu believers, black datura is associated with lord Shiva. Often, followers of Lord Shiva plant these plants in their homes to ward off evil and receive the blessings of Lord Shiva.
Health Benefits:
- Datura leaves contain atropine compounds that help in relieve asthma. Thus, in Nepal, many Sadhus smoke datura as a cigarette.
- The antiviral properties present in datura helps in fighting numerous viral diseases such as rabies.
- The antioxidant element present in datura helps in relieving chronic illnesses such as diabetes, stroke, atherosclerosis, cancer, and heart disease.
- The herb is an essential medicine in Ayurveda to treat psoriasis.
- Jatamansi/Spikenard
Information
| Scientific Name | Nardostachys jatamansi |
| Found in | 26 districts of Himalayan region |
| Flowering period | August to September |
| Color | Pink |
| Other name | Tapaswini or Bhulte |
| Parts used | Root, and rhizomes |
Native to the Himalayas, the spikenard has embodied one of the most sacred essences for thousands of years – because of its spiritual and medicinal properties.
The plant inhabits the humid regions of the Himalayas and grows naturally in Nepal, Bhutan, and Sikkim at heights between 3000 and 5000 meters. Varieties of spikenard also thrive in China and Japan.
The name “Jatamansi” means something like “giver of life” in Sanskrit and shows how highly valued this wonderful medicinal plant has always been in the ancient natural medicine, Ayurveda.
Health Benefits:
- Jatamansi improves hair growth and stops hair loss.
- Jatamansi helps relieve tension in the body, calm emotions, and help a person fall asleep soundly.
- Jatamansi is an indispensable stress reliever and mood enhancer due to its apoptogenic effects on the body. It is extremely helpful in treating stress-related headaches.
- Jatamansi is an excellent natural tonic for the skin, improving its structure and giving radiance.
- Jatamansi has anticonvulsant and antiarrhythmic activity, which is very important in reducing heart palpitations and symptoms of hysteria.
- Chiraito/Swertia
Information
| Scientific Name | Swertia |
| Found in | Ilam, Panchthar, Taplejung, Tehrthum, Sankhuwasabha, Dhankuta, Bhojpur, Makwanpur, Sindhuli, Ramechhap, Dolakha, Sindhupalchok, Gorkha, Salyan, Rolpa, Dolpa, Acham, Doti, Dandelura, Bajuradhura |
| Flowering period | July to November |
| Color | Lurid greenish-yellow, tinged with purple |
| Other name | Bhale chiraito (Nepali), khalu (Newari), khupli (Rai), leketite (Doteli) |
| Parts used | Whole |
Swertia grows as a perennial herb and reaches a height of 15 to 60 centimeters. The stem is palpably angular. The lower leaves are ovate and alternate and are reminiscent of plantain plants. The upper leaves are lanceolate, opposite, and smaller.
The swertia flowers bloom between July and August in a loose, raceme-like inflorescence. The steel blue to dull purple petals are separated almost to the bottom, spread out in a star shape, and a real feast for the eyes. Darker dots or stripes give them that certain something.
Leaf, root, stem, flower, and bark are all used as medicine.
Health Benefits:
- The whole part of the herb is useful in treating various diseases such as stomach aches, stomach worms (bugs/bites), fever, blood clots, wounds, and indigestion.
- It is used as a tonic to relieve menstrual pain and treat the menstrual disorder in women.
- The herb is especially beneficial for treating skin diseases and irritation, including acne, ringworm, bacterial growth, and cysts.
- The plant is also beneficial for curing several animal diseases.
- Panchaule
Information
| Scientific Name | Dactylorhiza hatagirea |
| Found in | Himalayan region |
| Flowering period | June to July |
| Color | Pink or purple |
| Other name | Salam panja or hattajadi |
| Parts used | Root |
Panchaule, scientifically known as Dactylorhiza hatagirea, is found in the Himalayan region of Nepal, where the herb is known as Hattajadi or Panchpate. The rhizome is divided into five parts resembling the human hands; thus, the herb popularly gained the name panchaule(Panch meaning five and Aule meaning fingers). Although the plant is not as popular as other medicinal herbs, it has been used in Ayurveda medicine since ancient times.
Growing at an altitude of 2500 meters to 5000 meters, the pink or purple flower blooms from June to July. Excessive exploitation and illegal foraging of the herb have led the IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) to categorize this plant under the category of endangered species.
Health Benefits:
- Beneficial in treating impotence and improving reproductive health.
- Helps in preventing chronic muscle pain.
- Beneficial in treating respiratory diseases, breathlessness, and weakness.
- It is beneficial for women to consume it after pregnancy. This cures their weakness and physical infirmity.
- It strengthens intestinal health and eliminates indigestion.
- Mucilage jelly obtained from the roots is used to treat dehydration, diarrhea, and chronic fever.
- Bojo/ Sweet flag
Information
| Scientific Name | Acorus calamus |
| Found in | Hilly areas of Nepal and Kathmandu |
| Other name | Flag root, sweet calomel, muskrat root, sweet flag, sweet sedge |
| Parts used | Root |
Bojo or Acorus calamus is a perennial herbaceous plant that grows wildly in the hilly areas of Nepal. Now, Kathmandu Valley residents have also started to plant the plant in their house gardens after recognizing its medicinal properties.
The root of the plant has numerous positive health benefits that help prevent various pathologies. The bojo roots are rich with essential oils that give the plant its unique smell and taste.
With the evolvement of Ayurveda medicine, bojo plants are also distinguished for their cosmetic properties. The medicines prepared from the components of the bojo plant have multiple medicinal and therapeutic purposes, but they also come with a small range of contraindications.
Health Benefits:
- The bojo plant helps n dilating heart blood vessels preventing and treating hypertension.
- The plant also has antispasmodic action helping alleviate pain in internal organs and muscles.
- Antimicrobial properties of the herb the body fight against bacterial infection.
- Stimulate the nerve function and eliminates stress and depression.
- Helpful in controlling internal and external bleeding.
- The astringent properties relieve the problems with the stool.
- Has a general stimulating effect and increases overall metabolism.
- Chiuri/ Diploknema
Information
| Scientific Name | Diploknema butyracea |
| Found in | Western Nepal such as Dadeldhura, Baitadi, Doti and Achham |
| Flowering period | Winter |
| Color | Light yellow |
| Other name | Indian butter tree |
| Parts used | Whole |
The Chiuri plant has been traditionally used in Nepal for a long time. Especially the plant holds an integral position among the Chepang community, who prefer to give their daughters the plant as a dowry during their wedding.
Among the several uses of the chiuri plant, the local community prepares sacred butter from its seeds which are still used to light lamps in the Buddhist monasteries. The chiuri plant can be 20 to 25 m tall and inhabit regions of an altitude of 1500 m above sea level.
The Chiuri plant is also an attraction for bees as its flowers’ sugar content is about 42%. Therefore, Chiuri is considered an essential source of honey production. Beekeepers move beehives to forests where these plants are found.
Chiuri is also used to make candles, soap, cream, juice, various cosmetic materials, wine, jam, honey, organic fertilizers, and pesticides.
Health Benefits:
- The chiuri butter has antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic properties; thus, the butter is used to relieve headaches and treat rheumatism.
- The leaves of this plant have an antibacterial and antifungal effect that can be used in acute dysentery.
- The compounds contained in the herb are also beneficial for controlling hemorrhage and relieving eczema and skin irritation.
- The tonics made from its flowers help promote lactation.
- Gurjo/ Giloy/Heart shaped moonseed
Information
| Scientific Name | Tinospora cordifolia |
| Found in | Almost all terrains from lowland forests of Terai to mid-hills |
| Flowering period | Monsoon season |
| Color | Light yellow |
| Other name | Guduchi, Chinnodbhava, or Galeya |
| Parts used | Stem |
Gurjo is a climbing shrub that has been an indispensable herb in Ayurvedic medicine. During the COVID 19 outbreak, gurjo suddenly gain the fame in Nepal for its medicinal values. The herb is in use since the ancient times for treating infection, fever, and diabetes.
The entire plant is beneficial and can be used for therapeutic purposes but its stem contains more valuable compounds.
The term Giloy according to Hindu mythology, refers to a mythical celestial elixir that helps the person remain forever young.
Health Benefits:
- Guduchi helps strengthen the immune system and contains biologically active compounds – alkaloids and lactones.
- It cleanses the body from toxins and calms your mind.
- Giloy helps to control the level of insulin production in your body. Guduchi can also burn excess glucose and lower blood sugar levels.
- Helps reduce breathing problems, colds, and coughs due to its anti-inflammatory properties.